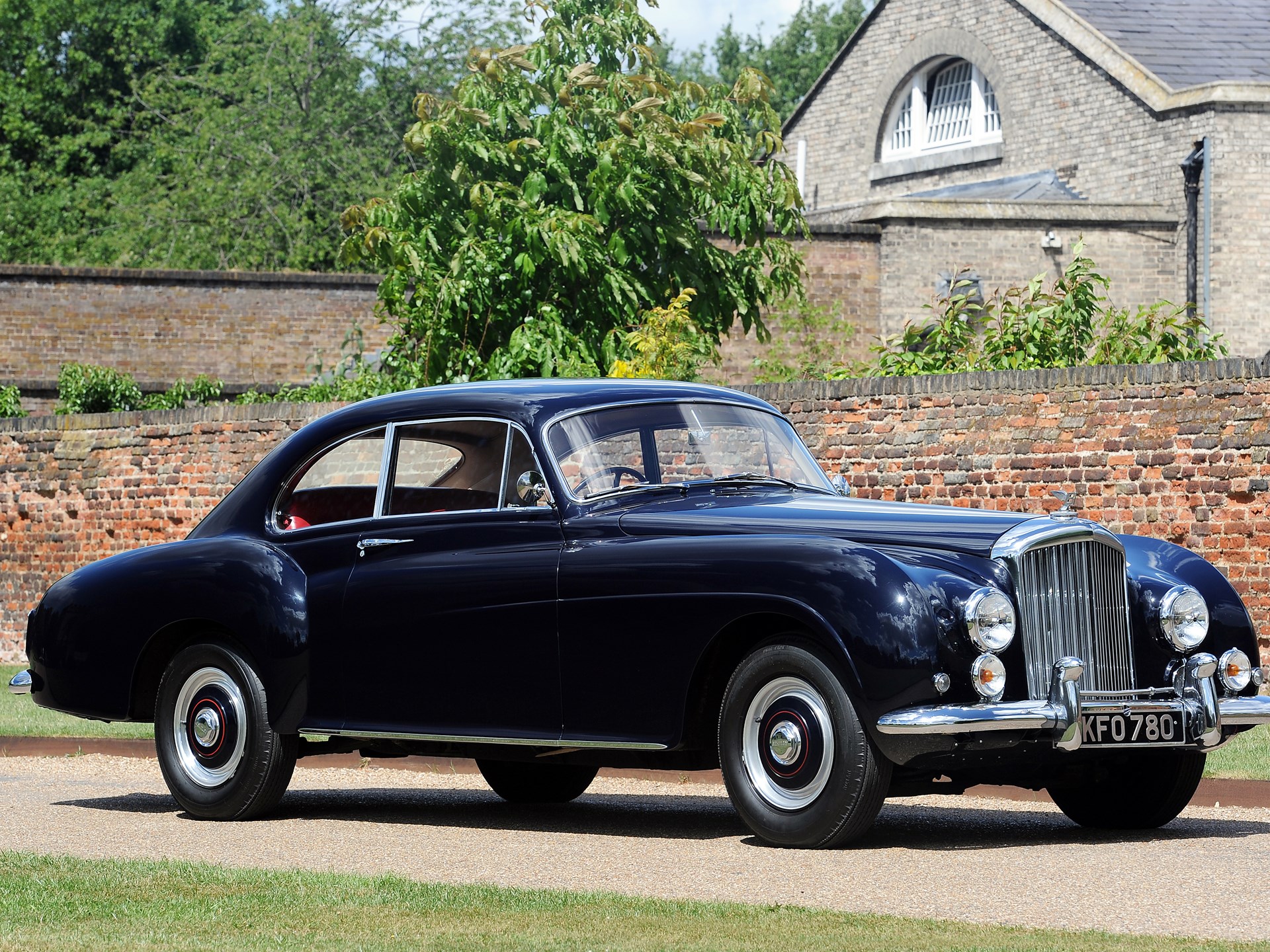
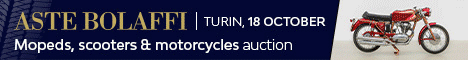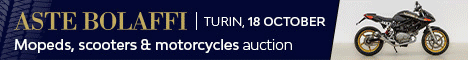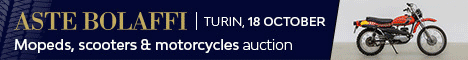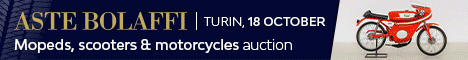
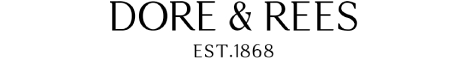1955 Bentley R-Type Continental
The R-Type Continental was a high-performance version of the R-Type. It was the fastest four-seat car in production at the time.
The prototype was developed by a team of designers and engineers from Rolls-Royce Ltd. and coachbuilder H. J. Mulliner & Co. led by Rolls-Royce's Chief Project Engineer, Ivan Evernden. Rolls-Royce worked with H. J. Mulliner instead of their own coachbuilding subsidiary Park Ward because the former had developed a lightweight body construction system using metal throughout instead of the traditional ash-framed bodies.
The styling, finalised by Stanley Watts of H. J. Mulliner, was influenced by aerodynamic testing conducted at Rolls-Royce's wind tunnel by Evernden's assistant, Milford Read. The rear fins stabilised the car at speed and made it resistant to changes in direction due to crosswinds.
A maximum kerb weight of 34 long hundredweight (1,700 kg; 3,800 lb) was specified to keep the tyres within a safe load limit at a top speed of 120 mph (190 km/h).
The prototype, with chassis number 9-B-VI[10] and registration number OLG-490, which earned it the nickname "Olga", was on the road by August 1951. Olga and the first series of production Continentals were based on the Mark VI chassis, and used a manual mixture control on the steering wheel boss, as these versions did not have an automatic choke.
The early R Type Continental has essentially the same engine as the standard R Type, but with modified carburation, induction and exhaust manifolds along with higher gear ratios. The compression ratio was raised to 7.25:1 from the standard 6.75:1, while the final gear ratio was raised (lowered numerically) from 3.41 to 3.07.